The rose is rightly considered the most beautiful among flowers, and is often a planted crop in flower beds. Its owners are anxious when they find yellow leaves on a pink bush, and for good reason - this is often a signal that there are some problems. We learn the rules for caring for roses, the various causes of yellowing of their foliage, what measures should be taken with this phenomenon, and also get acquainted with sustainable varieties of roses.
Basic rules for caring for roses
A rose will grow and develop normally if properly cared for.
To do this, you must adhere to the basic rules for caring for rose bushes:
- Buy a healthy seedling with a well-developed root system from a trusted, well-established manufacturer.
- The choice of place. This should be a place not blown by the winds and well lit by the sun. When determining places for planting pits, one should adhere to the recommended distances between the bushes, depending on the variety, type and purpose of the rose. Thicken planting is undesirable.
- Soil preparation. The acidity of the earth in which the rose bush will grow should be in the range of 5.5–6.5 pH. She should be nutritious, well permeable. Loams with a water depth of no closer than 1.5 m are best suited. A fertile top layer mixed with humus, peat or rotted manure, sand, and superphosphate (100 g / sq.) Are added to the planting pit 0.8–1 m deep. m.) and ash (up to 1 kg / sq. m).
- Soil care. You should regularly remove weeds and loosen the soil. You can mulch it - it will not only protect against weeds and drying out the soil, but also improve the composition of the soil.
- Timely watering. It is especially important to ensure sufficient soil moisture for newly planted plants that have not yet taken root. A well-rooted and grown bush already has a deep-lying root system and requires abundant and not frequent watering, but it is impossible to allow strong drying of the soil, since roses love moisture. It is necessary to water not with cold water in the morning or in the evening.
- Top dressing. Lack of nutrients, especially potassium and phosphorus, worsen the appearance of the flower and provoke the appearance of diseases.
- Preparing for the winter. In the fall, the plant is pruned and a covering material is used to protect it from frost. Usually the bushes are covered with a mixture of sawdust with organic matter (peat, humus, rotted manure), and on top they still cover with a film or spruce branches. In spring, shelter should be removed on time.
- Plant inspection and protection. Rose bushes should be inspected for the presence of diseases and pests. If they are detected, take timely control measures.
Why does the rose turn yellow leaves and what to do
The causes of yellowing of foliage in rose bushes are different. Often this is a signal of a violation of the rules for caring for rose bushes or of their defeat by diseases or pests. Especially strongly react to sudden changes and room roses growing in a limited environment get sick.
Nutrient deficiency
Improper nutrition leads to a deterioration in the development of the plant (slow growth, weakening, reduced resistance to disease) and causes yellowing of the foliage.

Moreover, with a lack of various elements and foliage, it turns yellow differently:
- Lack of potassium. Old leaves turn yellow early, starting from the upper parts and gradually moving to the edges. The edging of the leaves turns brown and dries over time, and the veins still have a green color. Then the sheet completely becomes reddish tones. For top dressing, potassium sulfate is used.
- Lack of nitrogen. The plant first slows down growth, turns pale, and then turns yellow. He urgently needs to do foliar top dressing with a urea solution or feed it with fertilizer with the presence of nitrogen (ammonium nitrate and complex).
- Calcium deficiency. It leads not only to yellowing of the foliage, but also to its fading and deformation. The tops of the bushes brighten and die. In this case, superphosphate or calcium nitrate is used.
- Lack of iron. Leaves turn yellow, starting at the edges, and at the end become almost white and fall off. The bushes should be sprayed at least 2 times with foliar top dressing containing iron (for example, Kemira Universal 2 or Ferovit) and add quickly decomposing organic matter.
- Magnesium deficiency. It appears first on old leaves, in the center of which lighter spots appear. Then, redness and yellowing appear between the veins, and the edges remain green. Old leaves fall, and yellowness passes to new ones. Under the bushes make magnesium sulfate or ash.
- Manganese deficiency. First, the places near the edge between the veins turn yellow, and the veins themselves remain framed by greenery. The plant is fed with manganese sulfate (can be foliar top dressing), acid fertilizers are applied.
Important! You should also not overfeed rose bushes with fertilizers. An excess of potassium leads to a delay in their growth, and an excessive content of nitrogenous fertilizers in the soil reduces resistance to fungal diseases.
Lack of sunlight
Among the varieties of roses there are plants that grow well in partial shade, but in general this flower does not tolerate shade. It begins to grow poorly, does not bloom and turns yellow. If you initially chose a shaded place for planting, then the source of the shadow should be removed, and if this is not possible, carefully transplant the rose to another place in early spring or autumn.
The rose is transplanted to a new, sunny place with a lump of earth, wrapping it in cloth or film. Long roots that interfere with the excavation of the bush can be chopped off. The seat is prepared in advance.
Wrong watering
With a lack of moisture, the leaves of the roses turn yellow and curl, the leaves dry at the edges, and the color is deformed and falls off. With a prolonged lack of water, a rose can stop flowering altogether.
Especially need more frequent watering roses growing in containers or pots. Limited capacity soil dries quickly. During the summer heat, container or house plants are watered every evening.
At the same time, pink bushes growing in containers should not be poured too often. They should not have stagnation of water, as this can cause rotting of the roots and chlorosis with yellowing.
When watering, seasonal temperatures should be considered. When it gets colder, the plant is watered less often. In an arid climate, home roses are recommended to be sprayed with water. For irrigation and spraying, do not use cold tap water. It must first be defended so that it is heated and purified from chlorine.
Did you know? Rose aroma is an adaptogen and an aphrodisiac. Rose oil is used to make perfumes and cosmetics.
Pests and diseases
The appearance of various lesions can also cause yellowing of the foliage. They are usually caused by pests and diseases of roses.
Consider the main pests:
- Spider mite. Red-brown insects located on the bottom of the leaf. Identified when a thin cobweb appears and yellowing of foliage, which subsequently withers and falls. The cause of the lesion is the dry weather, as well as the affected neighboring plants. To combat such insects, chemical treatments like Akarin, Actellik are used.
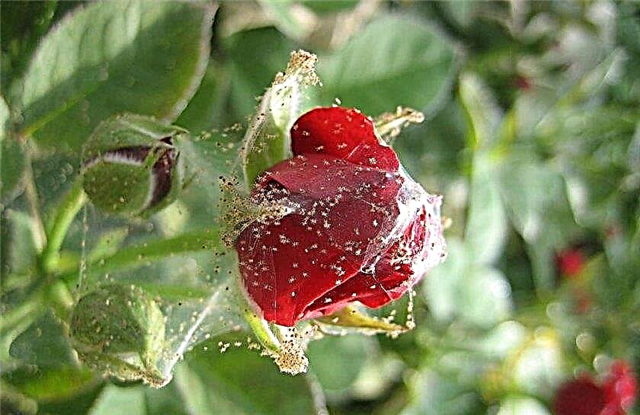

- The rose circadian. These are yellowish insects with wings. Identified by light spots on the leaves, which then fall off, the growth and development of the flower slows down. In hot weather, they multiply rapidly and can provoke the appearance of viral diseases. To eliminate this problem, leaves affected by the cicada remove and apply insecticides ("Aktara", "Fitoverm").

- Thrips. Very small insects that are not visible to the naked eye feed on the juice of flowers. The leaves are deformed and covered with dark spots. Hot weather and dry air can provoke the appearance. Humidity should be increased and chemical preparations should be applied (Actellik).

Bad weather conditions and improper care can cause the following diseases:
- Rust. This fungal disease is detected by a rusty coating on the bottom of the leaves. In this case, the affected areas are removed and chemicals such as Bordeaux fluid and Topaz are used.

- Black spotting. Brown spots of various shapes appear on the plant. It is important to carry out prophylaxis in the form of top dressing. The affected parts are eliminated, and the rose bush is treated with chemicals ("Profit", "Fitosporin").

- Powdery Mildew This fungal disease is detected when white-gray plaque appears on the leaves. The fungus grows well in warm, humid weather. Affected areas are removed and chemical preparations are used (Gamair).

With the timely identification and elimination of the above troubles, rose bushes can be saved, and they can still please with their color more than once.
Other reasons
The following factors can cause yellowing of rose leaves:
- temperature changes due to a sharp change in weather;
- groundwater comes close to the surface of the earth, which leads to root decay;
- application for irrigation of chlorinated and cold water;
- hot weather with burning plants in direct sunlight;
- age-related yellowing of foliage in old specimens.
Did you know? The oldest rose still grows in Hildesheim (Germany) at the walls of the local cathedral. Her age is already about 1 thousand years. It belongs to the wild species.
Preventative measures
To prevent yellowing of leaves in roses, gardeners recommend the following:
- Make timely nitrogen, phosphorus and potash fertilizers, as well as micronutrients.
- Water correctly plants, prevent drying out and excess moisture. It is especially important to ensure that watering is sufficient during budding and flowering. To defend water before watering.
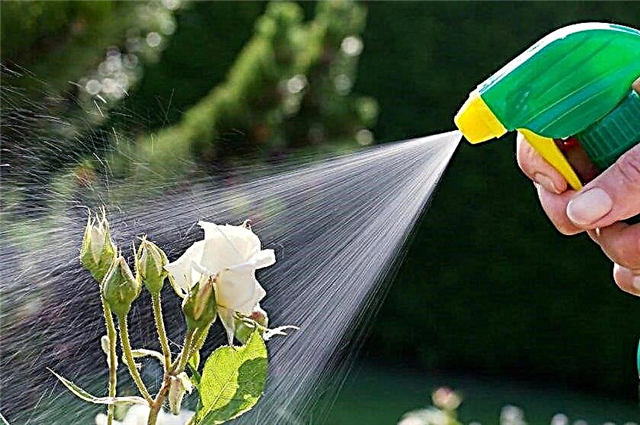
- Perform preventive treatment fungal and bacterial diseases, as well as insect pests. Regularly inspect plants and at the first sign of the appearance of diseases or pests take appropriate measures. To scare insect pests between rose bushes, you can plant lavender, marigolds, calendula. Insects cannot tolerate the smell of these flowers.

- Form bushes according to all the rules agricultural technology, to prevent excessive crowding. Rose planting is carried out according to the recommended schemes, depending on the variety. So, roses of small sizes are planted with an interval of 0.3 m, floribundas are planted at a distance of 0.5 m from each other, and curly and climbing ones - after 1.5-2.5 m
- Choose for landing varieties of roses that are resistant to various diseases.
- Pick a plot for planting correctly, given the composition of the soil, light exposure to sunlight, the location of groundwater.
Important! The root system of roses grows deep into the soil, so when choosing a site for planting, it should be taken into account that the groundwater level does not come closer than 1 m to the surface of the earth. Otherwise, the roots begin to rot, the leaves turn yellow, and the flowers die over time.
The most resistant varieties of roses
Now many nurseries offer various types of these beautiful flowers. Consider the most disease-resistant varieties.
Hybrid Tea Roses:
Floribunda:
Scrubs:
Climbing:
Yellowing of leaves in roses most often occurs due to improper care for them and with lesions by diseases or pests. It is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of rose bushes in order to timely solve all problems, as well as provide them with optimal conditions, use stable varieties.Did you know? Mankind has been breeding new varieties of roses since ancient times - already in ancient Roman times there were a dozen of them. Now there are approximately 30 thousand of their varieties, and the list is constantly updated.