The biggest enemy of honey bees is the tick. They can become infected with them on the flowers from which nectar is collected. To reduce the harm from parasites, it is necessary to take timely measures and destroy ticks. Read about how, what and when to process bees in this review.
Symptoms and diagnosis of infection
The fight against ticks is complicated by the fact that signs of infection may not be obvious at the initial stage. But, if you periodically inspect the bottom of the hive, you can find dead ticks on it - this is the first sign of infection. They lead to the death of the insect carrier, which means that at the bottom you will also find dead bees and drones. If the family is severely affected by pests, then there will be many of them.

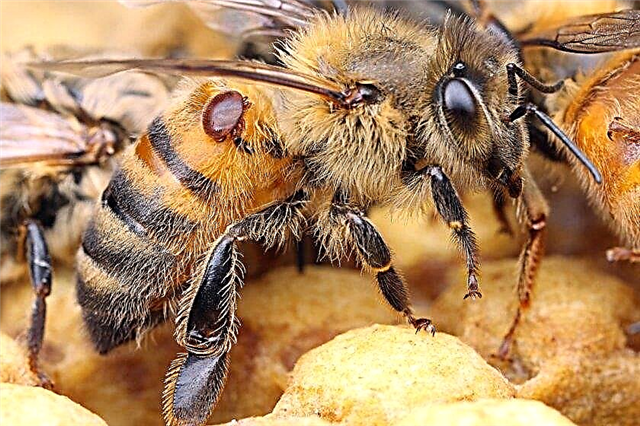
When developing, ticks weaken bees, parasitizing on them. Most species can be seen with the naked eye. They inhabit both adult insects and brood. Parasites hibernate on adult insects. Often they are between the chest and the abdomen.
Other signs of infection:
- visual presence of ticks;
- deformed or underdeveloped young bees;
- damaged wings in working individuals;
- insect weakness;
- death of families, especially young animals;
- decrease in honey collection.
Tick-borne affliction
Tick infection usually has similar symptoms and treatment methods, regardless of what kind of tick hit your wards. A small number of ticks infecting the colony does not cause much harm, but as they grow, the colony will weaken, and this will slow down the replacement of old individuals with new ones. The process of development of the brood will also slow down, and the general condition of the colony will worsen.

Infection is possible at any time of the year. When deciding what is the best way to process bees, consider the strength of the family (not all methods can be used for a weak colony) and seasonality. The use of toxic substances is not recommended during honey collection.
Beekeepers carry out 2 treatments as a means of prevention - in November, before leaving for wintering, and in early spring. Other regimens are used for treatment if there is evidence of infection.
Important! The action of various essential oils, drugs in the form of smoke or liquids irritates bees. They become more mobile and this causes shedding of ticks. Therefore, always supplement the treatment with a subframe to conveniently remove fallen pests from the hive.
Varroatosis
Varroatosis is considered one of the most devastating bee diseases in the world. The colonies are affected by the tick Varroa jacobsoni. He falls into the hive along with working individuals, from the flowers that they visit. The pest was first discovered in apiaries in Egypt; Since then, the disease has taken on the character of an epidemic and has spread widely.
The body width of the varroa tick is 1.8 mm. The pest is characterized by a transverse oval body shape, brown in the female and white in the male. The insect is like millet. The female has a life cycle of 2–3 months in summer and 5–6 in winter. On honey plants, it survives no more than 5 days without a carrier. The habitat is all living things in the hive - bees, pupae, drones. Lays eggs to the brood until the cells are sealed. The food source is hemolymph (insect blood).

A characteristic feature of varroatosis is anxiety of bees. When installing the hive for the winter, such individuals often fly out and feel uneasy. In the spring you can notice insects with perforated wings and underdeveloped ones that emerged from the cells. The disease is diagnosed by the massive fall of bees and drones, as well as the presence of live pests on bees.
One way to get rid of ticks is with a metal mesh subframe. When infected individuals fall to the bottom of the hive, ticks do not die and can be carried by healthy insects. The subframe prevents them from rising, since the ticks do not fly and can only attach to a bee that creeps past them. The subframe is installed 3 cm above the bottom of the hive. The optimum diameter of the cell can be no more than 2-3 mm. If you lay a film on the bottom and grease it with a layer of petroleum jelly, then the mite that fell from the dead bee will stick and die - but the bees will not be able to get on the pallet due to the small diameter of the cells. The subframe and the pallet are cleaned daily. This method helps to reduce colony contamination by 30%.
Important! If the solution used for washing is filtered through gauze, it can be used repeatedly.
The maximum number of ticks is in a sealed honeycomb. To destroy them, it is necessary to open the sealed cells and shake out the infected brood. And those parasites that could remain in the cells are washed off with a stream of water with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide or a 3% solution of acetic acid. The operation can be repeated after 14 days. This helps to reduce infection by 20-40%.
Euvarroz
Euvarrosis causes the tick Euvarroa sinhai Delfinado. It was first described in 1974. Signs of infection are similar to varroatosis. The difference between the parasite is that this type of tick has a rounded shape. It feeds on Euvarroa hemolymph, and propagates as well as varroa. The development period from an egg to an adult is 5 and 6-7 days for males and females. The female begins to mate and lay eggs several days after the first molt. Parasites attach to the abdomen of bees and infect brood.
The main signs of infection:
- anxiety of bees;
- case.

For treatment, all the methods used for varroatosis are suitable: a mesh subframe, a heat chamber for processing bees, and chemical preparations.
Acarapidosis
Acarapidosis is caused by the microscopic tick Acarapis Woodi and is accompanied by the weakening and death of bee colonies. The tick parasitizes in the trachea of honey bees, causing their death. Parasites penetrate into the large proto-thoracic trachea of all insects, live and breed in them, but can also be found in the head, chest and abdominal air sacs. Outside the bee's body, they do not survive.
It is believed that the tick was first discovered in 1904 on the Isle of Wight (UK). The parasite is 0.2 mm long and has a white oval body with a shiny smooth cuticle. It affects young bees under the age of 2 weeks. Also, like others, it feeds on hemolymph. As a result of infection, the bees weaken and mortality begins.
Did you know? Some honey bee species are genetically programmed to control ticks. They can remove infected pupae from a closed brood, including developing bees that are sealed inside the cells with a protective layer of wax.
You can diagnose infection by reducing the number of bee colonies and reducing honey collection. The tracheas of dead insects turn black. Usually a severely infected family dies by the end of wintering. Mostly infection occurs from bee to bee. The original source may be new individuals or uterus. Primary infection is possible in places with high dampness, where Acarapis woody can live.
If the apiary shows signs of infection with this parasite, then quarantine is imposed on it for a year, as well as on the other apiaries, which were within a radius of 5 km. Among the main control measures, treatment with acaricides — Nitrobenzene, Methyl Salicate, or Folbeks — is noted, although previously infected families were simply destroyed. 
The medicine is used in the form of an aerosol, for this the nest is expanded before the start of the procedure. The drug is administered in the evening, after all the bees return to the hive. After spraying the aerosol, all cracks are tightly closed. An excellent treatment result is shown by Folbeks. The release form of the drug is cardboard strips with a drug.
They are used once a week with a uniform interval, for example, in 7 days. The strip is set on fire and introduced into the hive, suspended between the frames or laid on a metal sheet. All cracks must be covered with clay and seal the bee house. The exposure time is 30 minutes, after which the tightness can be broken.
Terms of treatment
Tick infection can occur at any time of the year, but most often occurs in the summer. Therefore, before the colony leaves for the winter, it is necessary to take preventive measures and take care of the destruction of pests.
Important! Families are not processed during the period of active honey collection, so as not to spoil the available honey.
The peculiarity of wintering of bees with ticks is that in the cold season, ticks lose their ability to reproduce, but they still bother the bees and in the spring the bee family will be too weak. It is also necessary to check the level of infection of the colony in the spring before the start of removal from the winter hut. When dead insects are detected, a treatment cycle is carried out.
Bee Processing Methods
During the existence of beekeeping, physical, zootechnical, and chemical methods for controlling parasites have been developed. It is necessary to understand them in order to be able to apply correctly and in a timely manner.
Zootechnical methods
The simplest and most affordable zootechnical method is the destruction of a sealed brood. This can be done by the bees themselves or the beekeeper; the method consists in opening the sealed cells, shaking out the infected insects and treating the cells with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide or 3% solution of acetic acid.

The use of a stretcher to prevent the infection of healthy bees with ticks that have fallen from dead insects is also of great benefit.
Medication
Chemical methods consist of treating bees with various drugs that are approved for use. It can be both the long-used drugs “Timol”, “Folbeks”, and relatively recent ones: “Bipin”, “Amipol”, “Fetfor”, “Polysan”.
The drug "Timol" is available in the form of a colorless powder. It must be sprayed on the upper bars of the frames. Permissible air temperature during processing is from + 7 ° С to + 27 ° С. If the drug is used for treatment, then after a week the procedure is repeated. And with a strong infection, another spray is added.
Important! Do not forget to strictly adhere to the doses indicated in the instructions for the drug. In large volumes, drugs can contaminate honey, reducing its quality.
The Swiss drug Folbeks is a cardboard strip with a medicinal product applied to them. Spring processing is carried out if the outside temperature is at least + 12 ° C and the brood has not yet appeared.
To carry it out, you need to wait until in the evening all the bees are in the hive, seal the cracks and holes with clay. Through the lower notch, the Volbeks glow plate is fed on a metal sheet. Withstand processing time of 15 minutes. "Folbeks" is toxic, therefore observe safety measures during the work with chemical reagents.
"Bipin" is available in bottles in the form of a yellowish liquid, which has a specific pungent odor. It is used to treat varroatosis. The drug is mixed with water (0.5 ml per 1 liter of water) and the bees are sprayed with the resulting solution. The treatment is considered safe for bees and honey, but, nevertheless, treatment is recommended after the honey collection. Repeated spraying is recommended before wintering. It is forbidden to use for processing small families in which there are less than 5 brood frames.

Bipin T is an improved version of Bipin, also presented in bottles with a yellowish liquid. Dilution of the drug is performed according to the instructions. It is recommended to use it during autumn processing before installing hives for wintering. If there are dead insects in the spring, you can repeat the treatment procedure.
Amipol T is intended for tick control or prevention of varroatosis. It is delivered in the form of cardboard strips with the substance applied to them. The drug has no contraindications, so honey is completely suitable for consumption. In a typical scheme 2 treatments: spring and autumn. For small families use one strip, and for large - 2. Stripes must be hung between the frames. The exposure time is 30 days. Permissible air temperature is from 0 ° С to + 30 ° С.
Did you know? Bees control the thickness and transparency of their honey by flapping wings. In this way they regulate the evaporation of water. Therefore, the most transparent honey is obtained from strong families.
"Wertfor" is presented in the form of wood plates impregnated with the active substance. In the package you will find 10 plates. It is recommended to carry out spring and autumn treatment of hives with this drug. The plates are placed one for every 3 streets of the bees and left in the hive for a month. Such treatment cannot be used during honey collection. A single treatment with the drug is enough for one half year.
The release form of the Polysan preparation is small strips on which a therapeutic agent is applied. To activate it, the strips need to be set on fire. Processing is possible at temperatures from + 10 ° C to + 20 ° C. The technique of use is the same as that of Folbeks. For 10-12 frames, 1 strip is enough. Processing time - 60 minutes. The drug does not affect honey.

Folk remedies
Currently, the survival of bees is directly affected by their ability to withstand four main environmental factors:
- pesticides;
- ticks of varroa and other parasites;
- disease
- extreme weather conditions.
The modern practice of beekeeping largely depends on the use of chemicals to fight diseases. But as a result, viruses and parasites become stronger, and bee generations are weaker due to constant contact with chemicals.
Did you know? In nature, there are about 10,000 species of bees. But only 7 of them are melliferous.
Therefore, some beekeepers prefer to use old, but well-proven tools:
- formic acid;
- coniferous flour or gum juice from fresh needles;
- essential oils;
- turpentine;
- herbs;
- oxalic acid.
Formic acid is used to treat bee varroatosis. Processing is carried out at a temperature of + 10 ° C to + 30 ° C in early spring or summer after pumping out honey. Treatment occurs with acid fumes. It is installed in a subframe. The principle of operation is similar to a diffuser: a gauze wick is installed in the bottle, which is periodically wetted more intensely. The term of use is 10-15 days. When working with acids, observe safety precautions.
Oxalic acid is also used to treat ticks. It usually comes in the form of colorless crystals that are readily soluble in water. The drug is used in the form of a 2% aqueous solution, which is prepared before use. The treatment of insects is carried out by spraying. From 4 to 6 treatments can be carried out in a season at an ambient temperature of at least + 14 ° C. The interval between them is 12 days. Strict adherence to security measures is mandatory.

Some beekeepers are advised to carry out processing using essential oils. But, although they are safe for bees, using them is quite risky, because a bottle of concentrated essential oil can cause significant changes in the hive ecosystem. The technique of working with oil is similar to aerosol strips: you wet a strip in oil and place it in a hive. After placement, close the doors for 1-2 hours. Then open, but the strip can be left for another 3 days. Processing is possible at a temperature not lower than + 14 ° С.
Most beekeepers are familiar with using herbs in the hives. So, thyme gives 95% effectiveness against ticks of varroa, tracheal ticks and other parasites. For the same purpose, tansy flowers are used. Herbal treatment technology consists in kneading the grass to get more volatile and other active substances, folding it between the layers of gauze and placing it in a stretcher.The bookmark is kept for about 3 days, and then take a break of 5 days in order to allow those ticks to appear that were at the egg stage at the time of processing.
An effective remedy is the infusion of red hot pepper. For this, the dried pods are cut into pieces and brewed with boiling water (60 g per 1 liter of water). The broth is filtered and mixed with sugar syrup, prepared in a 1: 1 ratio. This top dressing is placed in the reach of bees. It is completely harmless to them, but for ticks it is dangerous. Processing is carried out three times with an interval of 10 days.
Pepper top dressing can be prepared without sugar. To prepare it, take 10 g of ground pepper and dissolve in 1 liter of boiling water, insist 15 minutes, filter and cool. This solution irrigate the honeycomb. Similarly, the infusion of coniferous flour works. For this, 1 kg of chopped needles (coniferous flour) is poured with 3 liters of boiling water for 2 hours. Then bred with sugar syrup (1: 1). Give the mixture to the pets every other day for 9 days. It is recommended to feed them in this way in early spring.
Heat treatment or smoke gun treatment
Physical methods are based on the use of heat. Bees are enclosed in a special chamber and exposed to heat. The temperature in the chamber should not be higher than + 48 ° C, the processing time should be no more than 15 minutes. Heat treatment will be good in early spring and late fall.
The outdoor temperature should not be higher than + 12 ° С - at this temperature the bees do not fly, and you can easily provide processing to the entire livestock. Also at this time, ticks are on the surface of carrier insects and will be easily destroyed. To do this, put a cassette with a funnel in front of the hive. The bees are shaken through a funnel into the cassette and set in a heated chamber. After treatment, they are shaken back to the hive.
To process bees from ticks, a smoke gun is also used. It is filled with a solution of a drug and fumigated by insects. Before spraying, the liquid heats up and is processed in pairs, almost the same as in a heat chamber. It is believed that it reduces the number of ticks by 90%. It is recommended to use in the summer after the completion of honey collection.
Did you know? Giant Himalayan bee honey is one of the most expensive in the world. It has hallucinogenic properties due to the rhododendrons from which it is collected.
Preventative measures
As ticks spread throughout the area, beekeepers believe that preventive measures are becoming increasingly important, which can at least minimize the risk of infection. First of all, it is worth considering the features of the landscape.

Tracheal mites love the lowlands and damp, and this must be considered when choosing a place to place the apiary. Plant repellents: tansy, wormwood, echinacea, which are not tolerated by ticks, will be a useful barrier next to your hives. Do not place bee houses closer than 500 m from highways, housing estates, and chemical industry enterprises.
Treat in spring before honey collection and in autumn before wintering. Most chemicals work well with ticks and are not toxic to honey insects. Follow the precautions and follow the instructions exactly, as any substance in large doses becomes poison.
Pay special attention to the health of new bees and get them only in trusted nurseries. If an infected hive is found, then you need to process not only it, but the rest of the apiary. The uterus in such a hive should be replaced with a new one.
Did you know? The average bee in its entire life produces only 1/12 teaspoon of honey.
Always pay close attention to the prevention of diseases and the healing of bees, especially when it comes to tick infection. This will keep families strong and ensure high productivity.