Geranium, or fragrant pelargonium, is one of the most popular house plants. This indoor flower pleases its owner not only with an elegant decorative look, but also with a whole range of all kinds of healthy qualities. However, it is not easy to grow it on the windowsill, it is believed that this plant belongs to a rather whimsical species. From this article you will learn in detail what odorous geranium is, and also get acquainted with its main requirements for growth and long flowering.
Botanical description of the plant
Fragrant geranium belongs to perennial herbaceous plants from the Geranium family. Tropical and subtropical regions of South Africa are considered to be the birthplace of the flower. In this area, the plant still lives in wild form. Today, this representative of the Geranievs is considered one of the most popular indoor plants, he has not only high decorative qualities, but is also actively used in folk medicine.
One of the main distinguishing features of this flower is the abundance of all kinds of varieties, which are characterized by a variety of aromatic qualities. Breeders bred hybrids with numerous small hairs, in contact with which the bush can emit the smells of mint, lemon and even an apple. These aromatic substances have a bactericidal effect, which further popularizes geranium.
The botanical characteristics of the plant are presented in the table below:
| Root system | Fibrous, with several main roots. Individual parts of the root system may form thickenings in which water and nutrients are stored. |
| Stem | Straight, branched, up to 1 m high |
| Leaf shape | Rounded, but the edges are strongly dissected, divided into 3-5 blades |
| Leaf color | All kinds of shades of green, some varieties are characterized by various inclusions of bright colors (white, red, etc.) |
| Flower shape | The flowers are rounded, with almost perfectly round petals. |
| Flower color | Depending on the variety, the flowers acquire shades of white, red, blue and pink flowers. |
| Fruit shape | Strongly elongated, with a characteristic sharpening at the end, the shape of the fruit resembles a crane beak |
| Fruit color | Shades of brown or green-brown tones |
Aromatic geranium blooms profusely; under optimal conditions, flowering can be observed from early spring and almost until the beginning of winter. At this time, large flowers with a diameter of up to 5 cm are formed on the bush. On each peduncle, one to three flowers are located, gathering in small racemose inflorescences. Up to 10 stamens with anthers grow on each flower. After flowering on a bush, a box fruit with numerous seeds ripens.
Did you know? Fragrant geranium is a natural means of combating domestic pests. Its smell is able to deter cockroaches, ants and other unwanted insects.
Properties for the human body
Geranium is one of the few plants that has been widely used for medicinal purposes for many decades. All kinds of flower extracts make it possible to restore important metabolic processes, as well as cope with the body with a variety of pathologies and environmental challenges. That is why cultivating a bush on a windowsill is considered a rather profitable occupation for health.

Benefits and healing properties
The plant has the following beneficial effects on the body:
- bactericidal;
- antitumor;
- insecticidal;
- antiseptic;
- restoring;
- antidiabetic;
- immunomodulatory.
- All kinds of means based on fragrant pelargonium are used to treat:
- pathologies of ENT organs;
- neuralgic disorders (as a sedative);
- manifestations of PMS and other gynecological problems;
- head lice;
- damage to the organs of the circulatory system, including internal bleeding;
- cuts and other damage to the skin (as a restorative and antitumor drug);
- ARVI (as a natural repellent).
Contraindications and harm
The health benefits of geraniums are undeniable, but the plant can also adversely affect the body.
- First of all, it is not recommended to use decoctions, infusions and other flower extracts for:
- individual intolerance to individual components, manifested by allergies;
- diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- acute and chronic hypotension.
 In case of non-compliance with general recommendations for use, including neglecting contraindications, odorant pelargonium remedies can aggravate the general condition of the body, cause allergic manifestations on the body. In addition, the plant is able to increase blood viscosity, which can ambiguously affect the circulatory system, affected by various pathologies. That is why such folk therapy must be coordinated with doctors.
In case of non-compliance with general recommendations for use, including neglecting contraindications, odorant pelargonium remedies can aggravate the general condition of the body, cause allergic manifestations on the body. In addition, the plant is able to increase blood viscosity, which can ambiguously affect the circulatory system, affected by various pathologies. That is why such folk therapy must be coordinated with doctors.Important! Elderly people and children under 12 years of age are not recommended to carry out therapeutic therapy based on pelargonium. In case of urgent need it is used with caution and only under the supervision of doctors.
Main varieties
Today there are a huge number of different varieties of plants, however, not all of them are considered popular among gardeners.
Most often on the windowsill you can find the following varieties of fragrant pelargonium:
- Lemon - different rough leaves with a slight pubescence, the flowers are small, purple-pink hue. Under optimal conditions, the plant is able to grow up to 1-2 m in height, so it is often used as a standard species. The plant has a distinctive lemon scent that is released after touching leafy hairs.
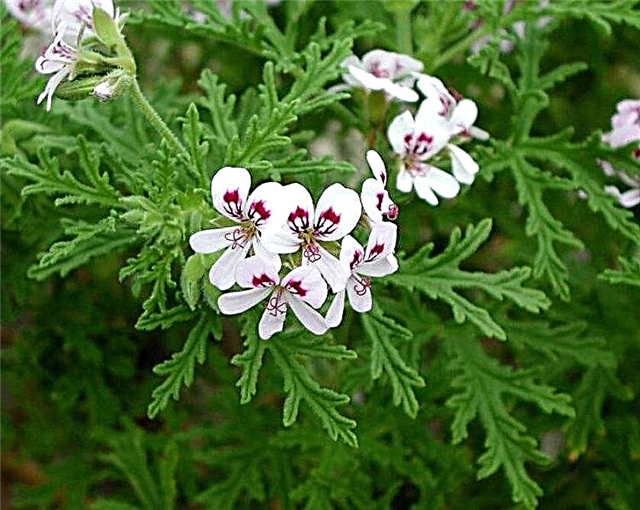

- Felt - undersized, compact bush, highly branched. The leaves are covered with numerous small hairs, which creates the effect of felt fabric. The flowers on the bush are formed small, pale white, with violet spots. A distinctive feature of the plant is a delicate mint smell, which is secreted by the green mass.

- Grapevine - an upright bush, about 90 cm high. The variety is named due to the special shape of the leaves, reminiscent of grape leaves. During flowering, white-pink or pink-purple flowers are formed on the bush, with bright stripes. The plant has a delicate smell, including notes of lemon and rose.
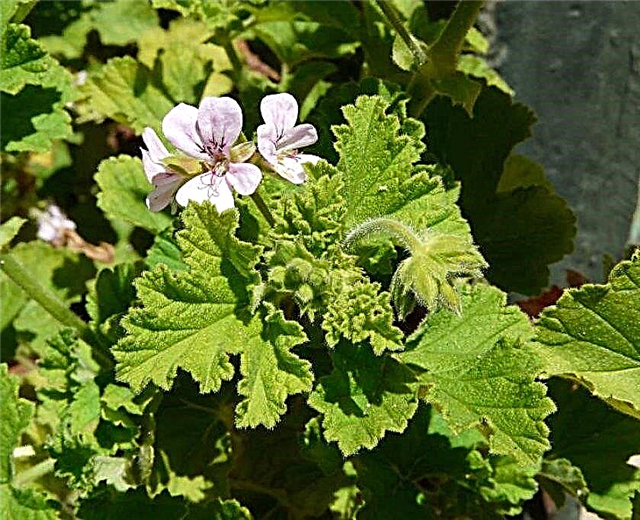

- Apple cider - a small flower, it is characterized by small rounded leaves with wavy edges, as well as small white flowers. The green mass has a delicate apple aroma, while the leaves emit a lemon pink aroma. The flower perfectly develops both indoors and in the flowerbed.

- Lady Plymouth - A small compact bush that is ideal for growing in pots and containers. The leaf plate is strongly dissected, has a white border around the edge. The flowers are medium sized, pale pink. They are characterized by a gentle, but distinct smell of a rose.
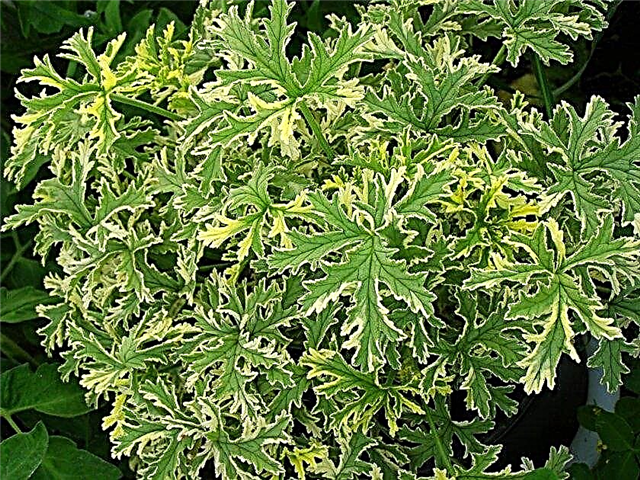

- Gray-haired lady - The flower is characterized by large dissected flowers of gray color, with a thin white border. A flowering bush is inconspicuous; small white flowers gather in small inflorescences on the shoots.

- Curly - Erect or climbing bush, up to 70 cm high. The stem is most often grassy, but eventually becomes woody. The sheet plate is cut, strongly twisted. Flowers develop white, lilac or pink. This geranium has a strong lemon aroma, therefore it is often used in cooking.

- Panicle - A small ornamental shrub, characterized by small white flowers, as well as small curly leaves. The foliage is characterized by a rather exotic smell, combining the aromas of mint, rose and nutmeg.
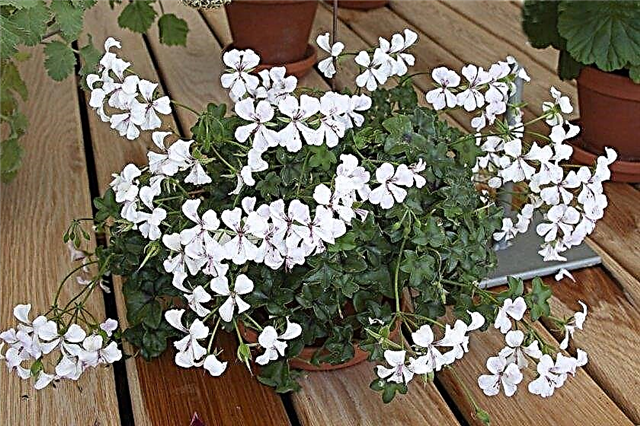

Growing conditions
To grow fragrant geraniums at home is quite possible. However, in order to achieve decorativeness, as well as elegant flowering, the plant needs regular care, as well as a special microclimate. To do this, the flower needs to be properly moistened, and also kept in optimal temperature conditions.
Lighting
All pelargoniums are considered photophilous plants, but they can also be successfully grown in partial shade. At home, the plant is placed on a windowsill with diffused color. Best for this are windows on the west or east side of the house. However, in spring, direct sunlight is not harmful to the bush, so it can be moved under intense sunlight, but not more than 4-6 hours.

Temperature mode
Like all tropical species, this plant is considered thermophilic. In summer, the optimal temperature indicator should be within +25 ... + 30 ° С, however, a flower can be successfully grown even at +20 ... + 24 ° С. In winter, pelargonium can be kept in a lower temperature range - +10 ... + 18 ° С.
Important! In summer, it is imperative to ensure that pelargonium does not overheat. To avoid this, during the summer drought, the flower is transferred to the coolest room in the northern part of the house.
Air humidity
Despite many conflicting opinions, geraniums do not like high humidity. Its sheet plate is capable of storing water, so an increase in humidity can provoke putrefactive lesions of the leaves. Typically, this indicator must be maintained at around 70%.
Home Care
Ornamental plants in most gardeners cause not only aesthetic pleasure, but also a lot of trouble. Most often, the conditions of the apartment do not meet all the necessary requirements in order to grow any kind of flora. That is why the successful cultivation of geraniums depends only on strict adherence to all conditions of its maintenance, including the basic care methods, which include proper watering, top dressing, transplanting and pruning.
That is why the successful cultivation of geraniums depends only on strict adherence to all conditions of its maintenance, including the basic care methods, which include proper watering, top dressing, transplanting and pruning.
Watering and spraying
Geraniums are watered sparingly, since this plant does not tolerate moisture oversaturation, while it perfectly resists short droughts. That is why in the summer the bush is watered no more than 2 times a week, and in winter the procedure is halved. Watering is carried out moderately, in small portions, for this use clean, settled water at room temperature. Humidify the substrate under the root, while spraying the bush and moistening the foliage when watering should be avoided, since in addition to damage by fungi, this can also provoke root rot.
Top dressing
Geranium requires regular top dressing. They are carried out already in 2-3 weeks after germination of young plants with an interval of 14-20 days. For fertilizer, you can use any complex mineral mixture for flowering plants based on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium compounds. They are introduced in liquid form and only under the root.
Important! Organic feeding for geraniums is prohibited, since they usually negatively affect the growth of the plant, and with intensive fertilizer can provoke its withering.
Pruning
 Pruning is important for any variety and variety of geranium. Only this procedure makes it possible to give the bush the necessary shape and size, as well as rejuvenate the flower. Most often, it is carried out in late February or early March, before the start of active vegetation.
Pruning is important for any variety and variety of geranium. Only this procedure makes it possible to give the bush the necessary shape and size, as well as rejuvenate the flower. Most often, it is carried out in late February or early March, before the start of active vegetation.
Large and old shoots, as well as all parts that spoil the decorativeness of the flower, including shoots formed from the sinus of leaves, are removed to adult plants. Thus, only those branches that are formed from root buds should remain on the bush.
Pinching the upper growth point is done to young plants. This procedure makes it possible to slow down the extension of the flower, which will help to create an elegant and compact bush. When germinating the cuttings, pinching is carried out in the phase of 8–10 leaves, while growing a flower from seeds — during the formation of 6–8 leaves.
Transfer
Geraniums are transplanted no more than once a year, before the start of active vegetation. The most favorable period for this begins from mid-February and lasts until mid-April. Usually this procedure is combined with pruning, which best prepares the bush for future flowering. The flower is transplanted into any garden container (plastic, metal, ceramic, glass), with a functional drainage hole. The new pot should be no more than 5 cm larger in diameter than the old container.

The soil for the flower must be fertile and loose. Any soil for flowering plants diluted with vermiculite, sand and perlite (2: 1: 1: 1) is suitable for this. You can also prepare the soil from humus, sod land and river sand (2: 2: 1).
Transplant as follows:
- Prepare a new pot, put a drainage layer (2-3 cm) of gravel or broken brick on its bottom, and then fill it with new soil 1/3.
- Remove the bush from the old tank along with a root layer of soil.
- Place the plant in a new pot, fill all openings with new soil, and then compact them.
- Water the container well, put the flower in the shade for 7 days.
How to propagate
Fragrant pelargonium propagates both vegetatively and generatively, so at home you can grow it from seeds, as well as parts of a bush. At the same time, the most effective and least time-consuming method is considered to be the method of obtaining daughter plants by cuttings or rooting of bush divisions. The best time for breeding pelargonium is considered the beginning of spring, only in this case you can get healthy and full-fledged sprouts.

Cuttings
To propagate the flower by cuttings, you need to perform the following steps:
- Separate the cuttings during pruning. They are the tops of shoots with 4 or more leaves.
- Soak cuttings in a solution of a growth stimulator for 6–8 hours (Zircon, Kornevin, etc.).
- Dip the cut into the water with a cut and place in a warm place (+20 ... + 26 ° С) until the roots appear.
- After the emergence of the rudiment of the root system, transplant the stalk into the soil. In the future, young seedlings are contained in the same way as adult plants.
Dividing the bush
Rooting of the shares is considered the easiest way to get a new plant. However, this method is only suitable if you already have an adult and large plant (at least 2-3 years old), which is ready for transplantation and separation into 2-3 parts.

They divide the bush during the spring transplant in this way:
- Take the bush from the pot and shake off the old soil.
- With a sharp knife, divide the bush into several parts. At the same time, about 30% of the old rhizome with viable buds and at least 1 shoot should remain on each part.
- Part of the bush is transplanted into a new pot (5 cm more in diameter than the volume of the root). They prepare it according to the same principle as for transplantation.
- The planted dividend is well moistened, and then grown in partial shade at a temperature of +22 ... + 26 ° С.
- A month later, the seedling is completely rooted, after which it can be fed.
Did you know? Geranium gained the greatest peak in popularity in the Victorian era (second half XIX century). At this time, in the UK, the plant was massively grown by both nobles and ordinary residents.
Seeds
Propagation by seeds is a more painstaking process, so you should resort to it with special care. Flower seeds germinate only in a special microclimate.
To germinate the seeds, the following manipulations should be carried out:
Recommended Reading

- Sanitize seed and soil.To do this, the seeds are soaked for 15-20 minutes in a 2% solution of potassium permanganate or 5-10 minutes in 70% alcohol. The soil is disinfected by roasting in the oven (+125 ... + 145 ° С, for 30–40 minutes) or by spilling the soil with a 2% solution of potassium permanganate.
- Prepare wide garden containers, fill them with sterilized soil. Any substrate for flowering plants diluted with river sand (2: 1) is best suited for this.
- Inoculate containers with planting material. To do this, it is sown in a row or hole method with a row spacing of 5 cm, to a depth of 1-2 cm.
- Pour the container well and cover with plastic wrap or glass, and then put it in a warm (+22 ... + 26 ° C) and well-lit place.
- After the appearance of the first shoots, remove the protective shelter, and in the phase of 2-3 leaflets dive seedlings into a separate container.
Growing difficulties
Usually caring for geraniums does not cause any difficulties for the flower grower, but often the plant can be sick if you neglect the conditions and cultivation techniques.

In most cases, this is accompanied by the following pathologies:
- yellowness of leaves - speaks of a lack of light;
- yellowness of leaves accompanied by drying out of leaves or wilting, - indicates violations of the regime and amount of watering;
- redness of the tips and edges of the leaves - The first sign of hypothermia of the bush;
- inhibition of flowering - observed in low light or in case of low temperature.
The main infectious diseases of fragrant geranium, their signs and treatment are presented in the table:
| Title | The main symptoms, treatment |
| Gray rot | The plant withers; various putrefactive inclusions of a gray-brown hue appear on shoots and leaves. Over time, the spots become covered with a light fungal coating. Treatment - treatment with a solution of "Fundazole" or "Vitaros" |
| Root rot | The plant slowly fades, yellowness of leaves appears. When examining the root system on the roots, putrefactive foci of a dark brown color are observed, often with a whitish coating. Treatment - treatment with a solution of "Homa", "Oksihoma", "Previkura" |
| Bacterial rot | The leaves are covered with putrefactive spots of brown color, over time they lead to curling and wilting of the leaves. Treatment - treatment with Oxychoma solution |
| Rust | The leaves are covered with yellow spots, on the back of which bright orange discharge occurs. Treatment - treatment with any fungicide |
| Viral Mosaic | The leaves turn yellow, covered with a mosaic pattern, the leaves curl and gradually dry. There is no cure. Sick plant must be destroyed |
The most common pests of geraniums include:
- Whitefly - small green bugs with white wings or caterpillars that cause wilting and twisting of leaves. Remove pests using the drug "Actara".
- Spider mite - the leaves curl and fade, a pale cobwebby coating appears on their back side. To control the pest, they use Akarin, Aktellik or Fitoverm.
- Powdery worm - a pale coating appears on the green mass, on which small oblong insects of white color are visible, the foliage fades and dries. The plant is sprayed with a soap-alcohol solution.
- Nematode - the plant lags behind in growth, the growth of the root mass is almost completely stopped, flowering and activity of the growth of buds are also inhibited. With prolonged exposure, the flower dies.
Fragrant geranium is not only an attractive ornamental plant, but also a valuable medicinal species. Today, many people decide to grow this plant, but not everyone succeeds in cultivating it for many years. This is explained by the fact that the flower requires not only painstaking care, but also daily attention.